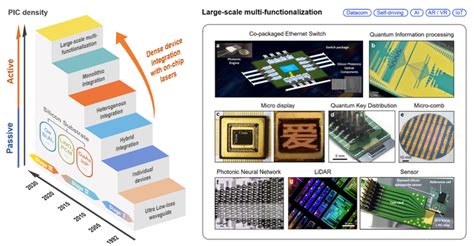
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, the demand for faster and more efficient data processing has never been greater. Data centers, the backbone of modern computing, are under constant pressure to keep up with the growing volume of data being processed. Enter Intel’s Silicon Photonics, a groundbreaking technology that promises to revolutionize the way data centers operate. This article delves into Intel’s roadmap for Silicon Photonics and its potential impact on the data center industry.
**The Need for Speed**

The traditional copper interconnects used in data centers have reached their physical limits. As data centers scale up, the number of copper connections required to transfer data between servers and switches becomes increasingly complex and inefficient. This has led to bottlenecks that can slow down data processing and increase energy consumption.
Silicon Photonics offers a solution by using light to transmit data. Light-based communication systems can achieve higher data rates and greater distances than copper-based systems, which makes them ideal for the high-speed, high-density environments found in modern data centers.
**Intel’s Silicon Photonics Technology**
Intel has been at the forefront of developing Silicon Photonics technology. The company’s roadmap for Silicon Photonics focuses on creating a new class of integrated photonic devices that can be manufactured using the same techniques used to produce microchips.
These devices, known as photonic chips, integrate both optical and electronic components on a single silicon chip. This integration allows for the creation of complex photonic circuits that can perform tasks such as modulating, amplifying, and routing light signals.
**Key Milestones in Intel’s Roadmap**
1. **2009**: Intel announces the first working Silicon Photonics device, a silicon-based laser that operates at 40 gigabits per second (Gbps).
2. **2012**: Intel demonstrates a 100Gbps data link using its Silicon Photonics technology, marking a significant leap in data center connectivity.
3. **2014**: Intel unveils its first 100Gbps transceiver, a critical component for connecting servers and switches in data centers.
4. **2018**: Intel showcases a 50Gbps Ethernet transceiver, designed to provide high-speed connectivity for servers and storage systems.
5. **2020**: Intel reveals a 400Gbps transceiver, a major milestone that brings the company’s Silicon Photonics technology to the forefront of data center innovation.
**The Benefits of Silicon Photonics in Data Centers**
The adoption of Silicon Photonics in data centers offers several significant benefits:
– **Increased Bandwidth**: Photonic chips can achieve data rates up to 400Gbps, significantly higher than copper-based solutions.
– **Reduced Latency**: Light-based communication systems have lower latency than copper, resulting in faster data processing.
– **Energy Efficiency**: Photonic systems consume less power than copper-based systems, reducing the overall energy footprint of data centers.
– **Scalability**: Silicon Photonics allows for the easy scaling of data center networks as demand for bandwidth grows.
**The Future of Silicon Photonics**
Intel’s roadmap for Silicon Photonics is ambitious and full of potential. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even higher data rates, greater energy efficiency, and more advanced photonic devices. The future of data centers looks bright, with Silicon Photonics playing a pivotal role in driving innovation and efficiency in the industry.
In conclusion, Intel’s Silicon Photonics technology is poised to transform the data center landscape. By offering faster, more efficient, and more scalable solutions, Silicon Photonics will be a key enabler in the next generation of data center infrastructure.