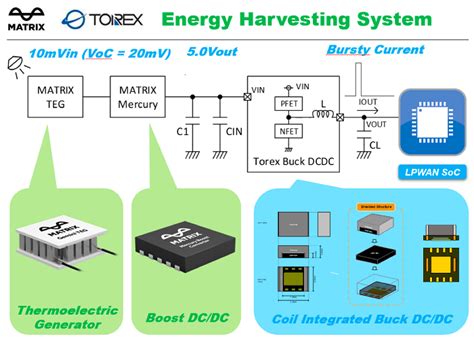
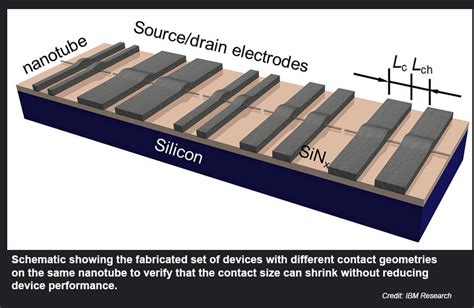
Introduction:
In the era of the Internet of Things (IoT), the demand for energy-efficient devices is increasing. Battery-free IoT devices have gained significant attention due to their potential to eliminate the need for regular battery replacements. Radio Frequency (RF) energy harvesting has emerged as a promising technology for powering such devices. This article highlights the recent milestones achieved in the efficiency of battery-free IoT RF energy harvesting.

1. Technological Advancements in RF Energy Harvesting
Over the years, significant advancements have been made in RF energy harvesting technology. Researchers have developed various methods to improve the efficiency of RF energy conversion, including:
– Antenna Design: Innovations in antenna design have led to increased efficiency and range in RF energy harvesting. Metamaterial-based antennas, for instance, offer higher gains and reduced dimensions.
– Matching Networks: The implementation of high-quality matching networks has optimized the conversion efficiency of RF energy into usable power. Advanced circuit techniques and components have improved the match between the antenna and the rectenna (rectifying antenna).
– Rectifier Technology: The development of high-efficiency rectifiers, such as Schottky diodes, has boosted the overall efficiency of RF energy harvesting systems. New rectifier technologies, like tunnel diodes, have further enhanced the conversion efficiency.
2. Milestones in Efficiency Improvement
Recent years have witnessed remarkable progress in the efficiency of battery-free IoT RF energy harvesting. Some of the notable milestones include:
– Record Efficiency: In 2019, researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology achieved an RF energy harvesting efficiency of 94.5% using a 3.1GHz antenna. This marks a significant milestone in the field, as it approaches the theoretical maximum efficiency of a perfect rectifier.
– Low-Power Devices: The efficiency of RF energy harvesting systems has been enhanced for low-power IoT applications. For instance, researchers have developed a rectenna that achieves 60% efficiency at 1.5GHz, making it suitable for powering ultra-low-power sensors and tags.
– Wearable Devices: Advancements in RF energy harvesting efficiency have enabled the development of wearable devices that can be powered wirelessly. For example, a flexible RF energy harvester has been demonstrated to power a wearable fitness tracker with an efficiency of 50% at 2.45GHz.
3. Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the remarkable progress in RF energy harvesting efficiency, challenges still need to be addressed to achieve widespread adoption in the IoT sector. Some of these challenges include:
– Frequency Selectivity: RF energy harvesting systems are highly sensitive to the frequency of the incident wave. Ensuring stable operation across various frequency bands remains a challenge.
– Integration: Integrating energy harvesting components into the overall system architecture requires careful design to ensure minimal energy loss.
– Scalability: As the number of battery-free IoT devices increases, scaling up the production of energy harvesting systems while maintaining efficiency becomes crucial.
Looking ahead, ongoing research efforts are expected to further enhance the efficiency of battery-free IoT RF energy harvesting. With the continuous development of advanced materials, components, and circuit design, the future holds promise for even higher efficiency and wider application of RF energy harvesting technology in the IoT ecosystem.