Introduction:
In the ever-evolving world of wireless networking, Wi-Fi mesh protocols play a crucial role in ensuring seamless connectivity across multiple devices. Among the various protocols available, 802.11kvr and proprietary roaming efficiency stand out as two prominent options. This article aims to compare and contrast these two protocols, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses in terms of roaming efficiency.

802.11kvr:
802.11kvr is a standardized Wi-Fi mesh protocol that was introduced by the Wi-Fi Alliance. It is designed to improve the performance and efficiency of Wi-Fi networks by optimizing the handover process between different access points (APs) within a mesh network. Here are some key aspects of 802.11kvr:
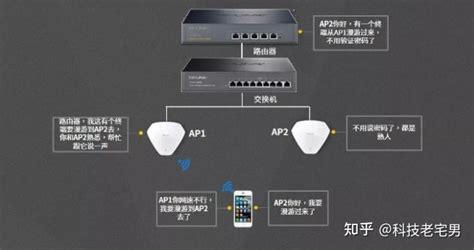
1. Handover Optimization: 802.11kvr enhances the handover process by reducing the time required for a device to switch from one AP to another. This is achieved by exchanging information between APs, enabling them to predict the optimal handover time and minimize the disruption to the user’s experience.
2. Load Balancing: The protocol ensures that the network load is evenly distributed across all APs, preventing any single AP from becoming a bottleneck. This results in improved overall network performance and reduced congestion.
3. Roaming Efficiency: 802.11kvr improves roaming efficiency by reducing the time and effort required for a device to find and connect to a better-quality AP. This is achieved by providing a list of available APs with their respective signal strengths, enabling the device to make an informed decision about the best AP to connect to.
Proprietary Roaming Efficiency:
Proprietary roaming efficiency refers to the roaming capabilities offered by specific vendors or manufacturers. Unlike 802.11kvr, these protocols are not standardized and may vary significantly across different vendors. Here are some aspects of proprietary roaming efficiency:
1. Customization: Proprietary protocols allow vendors to tailor the roaming process to their specific network infrastructure and requirements. This can result in better performance and efficiency in certain scenarios.
2. Integration: Proprietary protocols can be more seamlessly integrated with the vendor’s other networking solutions, such as security and management systems, providing a cohesive and efficient network ecosystem.
3. Limited Interoperability: One of the drawbacks of proprietary protocols is their limited interoperability with other vendors’ equipment. This can restrict the flexibility and scalability of the network, as well as increase the cost of deployment and maintenance.
Comparison:
When comparing 802.11kvr and proprietary roaming efficiency, several factors should be considered:
1. Standardization: 802.11kvr is a standardized protocol, ensuring interoperability and compatibility across different vendors and devices. Proprietary protocols may offer more customization but may lack this interoperability.
2. Performance: 802.11kvr has been designed to improve the overall performance of Wi-Fi networks, including handover optimization and load balancing. Proprietary protocols may offer better performance in specific scenarios but may not necessarily be superior in all cases.
3. Cost: Proprietary protocols may come with higher costs due to their customization and integration capabilities. 802.11kvr, being a standardized protocol, may be more cost-effective for large-scale deployments.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, both 802.11kvr and proprietary roaming efficiency offer unique advantages and disadvantages. While 802.11kvr provides standardized interoperability and improved performance, proprietary protocols offer customization and integration benefits. The choice between these two protocols ultimately depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the network deployment.