Introduction:
When it comes to upgrading your computer’s storage, an SSD (Solid State Drive) is often the go-to choice for faster boot times, quicker application launches, and overall improved performance. However, there are some common pitfalls associated with SSD upgrades, particularly when dealing with QLC (Quad-Level Cell) drives. In this article, we’ll discuss the issues of QLC cache exhaustion and the speed cliff, providing you with the necessary insights to avoid these traps.

1. Understanding QLC Cache Exhaustion
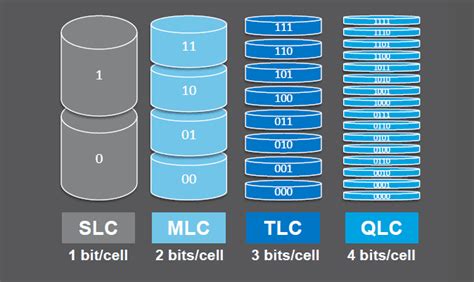
QLC (Quad-Level Cell) drives are a newer type of SSD that offer increased storage capacity at a lower cost per gigabyte compared to other types of SSDs, such as TLC (Triple-Level Cell) and MLC (Multi-Level Cell). However, this increased capacity comes at a price: a smaller cache size.
The cache is a small, high-speed storage area on an SSD that stores frequently accessed data. When the cache is full, the drive must write data to the slower main memory, causing a decrease in performance. This is known as cache exhaustion.
1.1 Causes of Cache Exhaustion
There are several factors that can contribute to QLC cache exhaustion:
– High levels of random writes: QLC drives are not as efficient at handling random writes as other types of SSDs, which can quickly fill up the cache.
– Insufficient cache size: QLC drives often have a smaller cache size than their TLC or MLC counterparts, making them more susceptible to cache exhaustion.
– Inadequate firmware optimization: Some QLC drives may not have the most efficient firmware, which can lead to increased cache exhaustion.
1.2 Avoiding Cache Exhaustion
To avoid the pitfalls of QLC cache exhaustion, consider the following tips:
– Opt for a QLC drive with a larger cache: While QLC drives with larger caches are more expensive, they can help mitigate the issue of cache exhaustion.
– Minimize random writes: Use tools like TRIM to optimize your SSD’s performance by clearing out unnecessary data from the cache.
– Choose a reputable brand: Look for SSDs from reputable manufacturers that have optimized their firmware for better cache management.
2. The Speed Cliff
The speed cliff refers to a significant decrease in performance that occurs on some SSDs after a certain amount of data has been written to the drive. This decrease in performance is usually due to the wear leveling process, which spreads out data across the drive to prevent excessive wear on specific cells.
2.1 Causes of the Speed Cliff
The speed cliff can occur for several reasons:
– Excessive writes: As mentioned earlier, excessive writes can lead to the speed cliff.
– Inefficient wear leveling: Some SSDs may not have the most efficient wear leveling algorithms, causing the speed cliff to occur more quickly.
– Old firmware: Outdated firmware can cause the speed cliff to occur at a lower threshold, leading to decreased performance.
2.2 Avoiding the Speed Cliff
To avoid the speed cliff, consider the following tips:
– Monitor your SSD’s write count: Keep an eye on your SSD’s write count and replace it when necessary.
– Update your SSD’s firmware: Make sure to install the latest firmware updates for your SSD to improve wear leveling and performance.
– Choose a reputable brand: Look for SSDs from reputable manufacturers that have optimized their wear leveling algorithms and firmware to prevent the speed cliff.
Conclusion:
While SSD upgrades can significantly improve your computer’s performance, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential pitfalls associated with QLC drives, such as cache exhaustion and the speed cliff. By understanding these issues and taking the necessary precautions, you can ensure that your SSD upgrade provides the desired performance boost without any unwanted surprises.