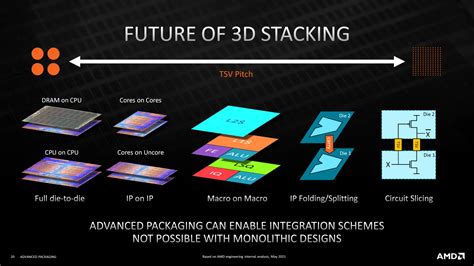
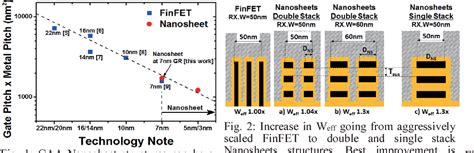
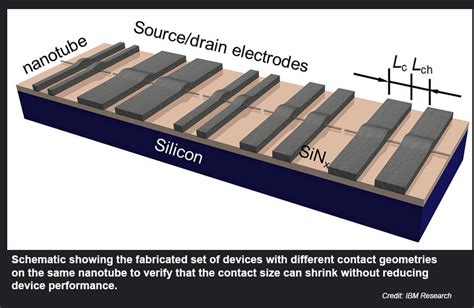
In the ever-evolving world of technology, the race to innovate and push the boundaries of computing power has never been more intense. One of the latest frontiers in this race is the development of 3D stacked CPUs, a technology that promises to revolutionize the way we think about computing. In this article, we will delve into the vertical integration race between AMD and Intel, as they both strive to be the pioneers in this groundbreaking technology.
The Emergence of 3D Stacked CPUs

3D Stacked CPUs, also known as 3D ICs (Integrated Circuits), are a significant leap forward in semiconductor technology. Unlike traditional 2D CPUs, which have components laid out flat on a single die, 3D stacked CPUs stack multiple layers of transistors, memory, and other components vertically. This vertical integration allows for greater density, higher performance, and improved energy efficiency.
AMD and Intel: The Rivalry Intensifies
As the pioneers in the CPU market, AMD and Intel have been locked in a fierce rivalry for years. With the advent of 3D stacked CPUs, the competition has intensified, as both companies aim to be the first to bring this revolutionary technology to market.
AMD: The Early Leader
AMD has been a leader in the development of 3D stacked CPUs, with its Zen 4 architecture featuring a 3D stacking technology known as Chiplet. This technology allows AMD to combine multiple smaller dies, each with its own CPU cores, cache, and I/O, into a single, powerful CPU. The result is a CPU that offers superior performance and efficiency compared to traditional 2D designs.
Intel: Catching Up with 3D Foveros
While AMD has been ahead in the 3D stacked CPU race, Intel has been working hard to catch up. The company has developed its own 3D stacking technology called Foveros, which allows for the vertical integration of components. Intel’s first 3D stacked CPU, the Intel Core i9-12900K, has already been released, and it is expected to deliver significant performance improvements over its 2D predecessors.
The Benefits of 3D Stacked CPUs
The adoption of 3D stacked CPUs brings several benefits to the computing industry. Some of the key advantages include:
1. Increased Performance: By stacking multiple layers of components, 3D stacked CPUs can offer higher performance and better multitasking capabilities.
2. Improved Energy Efficiency: Vertical integration allows for more efficient power management, resulting in lower energy consumption and longer battery life for mobile devices.
3. Enhanced Scalability: 3D stacking technology enables manufacturers to scale up CPU performance without increasing the size of the die, making it easier to create more powerful CPUs.
The Future of 3D Stacked CPUs
As AMD and Intel continue to push the boundaries of 3D stacked CPUs, we can expect to see even more impressive advancements in the coming years. The potential for this technology is vast, and it could lead to significant breakthroughs in various computing applications, from gaming and artificial intelligence to data centers and mobile devices.
In conclusion, the vertical integration race between AMD and Intel in the 3D stacked CPU market is a testament to the relentless pursuit of innovation in the technology industry. As both companies continue to push the limits of what is possible, we can look forward to a future where computing power is more accessible, efficient, and powerful than ever before.