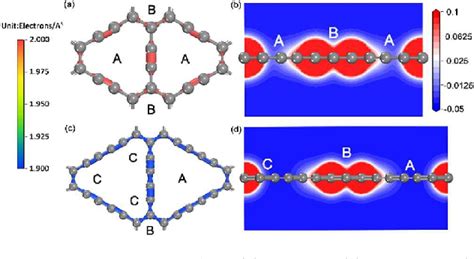
In the rapidly evolving field of battery technology, the quest for more efficient, durable, and powerful batteries has led researchers to explore unconventional materials. One such material that has garnered significant attention is graphyne, a two-dimensional carbon allotrope with a unique structure resembling graphene. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have paved the way for the design of novel materials, including graphyne, which could revolutionize battery anodes for next-generation energy storage systems.
Graphyne, a two-dimensional carbon material, is formed by the hexagonal arrangement of carbon atoms, similar to graphene. However, the difference lies in the presence of sp2 and sp3 hybridized carbon atoms, which gives graphyne a distinctive structure and properties. This unique structure is believed to offer several advantages over traditional battery anode materials, such as silicon and lithium metal.

One of the primary challenges in battery technology is the degradation of anode materials during the charge-discharge cycle. This degradation leads to a decrease in battery capacity and lifespan. Graphyne, however, is expected to address this issue due to its excellent mechanical and electrical properties. The following points highlight the potential of AI-designed graphyne for next-generation battery anodes:
1. High electrochemical stability: Graphyne exhibits a high electrochemical stability window, which means it can withstand the high voltage conditions typically encountered in battery operation. This property ensures that the material remains durable and maintains its performance over an extended period.
2. High theoretical capacity: Graphyne has a significantly higher theoretical capacity compared to conventional anode materials. This higher capacity translates to longer-lasting batteries with reduced charging times.
3. Excellent conductivity: Graphyne possesses high electrical conductivity, which is crucial for efficient charge and discharge processes. This property ensures that the battery can quickly charge and discharge, thus reducing the overall charging time.
4. Low cost and environmental friendliness: Graphyne is derived from carbon, which is abundant and inexpensive. Additionally, its production process is relatively simple and environmentally friendly, making it an attractive candidate for battery anode materials.
The role of AI in the design of graphyne for next-generation battery anodes is undeniable. AI algorithms have been used to simulate and analyze the electronic structure of graphyne, optimizing its properties for battery applications. This process involves the following steps:
1. Data collection: Researchers gather data on various carbon-based materials, including graphyne, to train the AI algorithm.
2. Feature selection: The algorithm identifies the most critical features that influence the material’s performance as an anode.
3. Optimization: Using the selected features, the AI algorithm explores different combinations to find the optimal graphyne structure for battery anodes.
4. Simulation and analysis: The AI-generated graphyne structures are simulated using computational methods to assess their properties and performance as anode materials.
5. Experimentation: The AI-designed graphyne materials are synthesized and tested in laboratory settings to validate their performance.
In conclusion, the AI-designed graphyne material holds immense potential for next-generation battery anodes. With its high electrochemical stability, high theoretical capacity, excellent conductivity, and environmental benefits, graphyne could revolutionize the battery industry. As AI continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in battery technology, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable energy storage solutions.