Introduction:
In the realm of power delivery circuits, capacitors play a crucial role in ensuring stable and efficient power supply. Two primary types of capacitors are widely used: solid and electrolytic capacitors. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, particularly in terms of lifespan. This article aims to explore the lifespan of solid and electrolytic capacitors in power delivery circuits, highlighting their differences and implications.

Solid Capacitors:
Solid capacitors, also known as ceramic capacitors, are known for their excellent stability, low ESR (equivalent series resistance), and high reliability. They are commonly used in various applications, including power delivery circuits.
Lifespan of Solid Capacitors:
The lifespan of solid capacitors in power delivery circuits can vary depending on several factors, such as the quality of the capacitor, operating temperature, and voltage ratings. Generally, solid capacitors have a longer lifespan compared to electrolytic capacitors.
1. Quality: High-quality solid capacitors can last for tens of years, while lower-quality ones may have a shorter lifespan.
2. Operating Temperature: Solid capacitors are less susceptible to temperature variations, which can significantly impact their lifespan. Operating within the recommended temperature range can extend their lifespan.
3. Voltage Ratings: Solid capacitors with higher voltage ratings tend to have longer lifespans, as they can handle more stress.
Advantages of Solid Capacitors:
– Excellent stability and low ESR
– High reliability
– Suitable for high-frequency applications
– Less susceptible to temperature variations
Disadvantages of Solid Capacitors:
– Higher cost compared to electrolytic capacitors
– Limited capacitance values
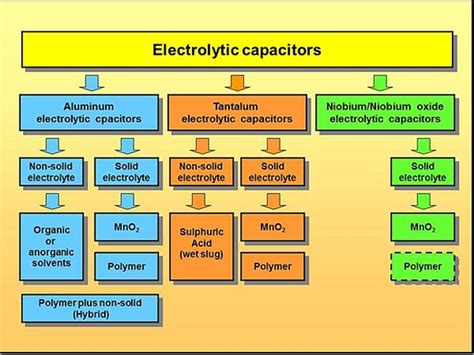
Electrolytic Capacitors:
Electrolytic capacitors are widely used in power delivery circuits due to their high capacitance values and low cost. However, they have a shorter lifespan compared to solid capacitors.
Lifespan of Electrolytic Capacitors:
The lifespan of electrolytic capacitors in power delivery circuits is influenced by several factors, including the quality of the capacitor, operating temperature, and voltage ratings.
1. Quality: High-quality electrolytic capacitors can last for several years, while lower-quality ones may have a shorter lifespan.
2. Operating Temperature: Electrolytic capacitors are more sensitive to temperature variations, which can significantly impact their lifespan. Operating within the recommended temperature range is crucial.
3. Voltage Ratings: Electrolytic capacitors with higher voltage ratings tend to have longer lifespans, as they can handle more stress.
Advantages of Electrolytic Capacitors:
– High capacitance values
– Low cost
– Suitable for low-frequency applications
Disadvantages of Electrolytic Capacitors:
– Limited stability and higher ESR
– Reliability issues due to electrolyte aging
– Susceptible to temperature variations
Conclusion:
In power delivery circuits, the choice between solid and electrolytic capacitors depends on the specific requirements of the application. While solid capacitors offer longer lifespans and excellent stability, electrolytic capacitors provide high capacitance values at a lower cost. It is essential to consider the operating conditions and the importance of lifespan when selecting capacitors for power delivery circuits.