Introduction:
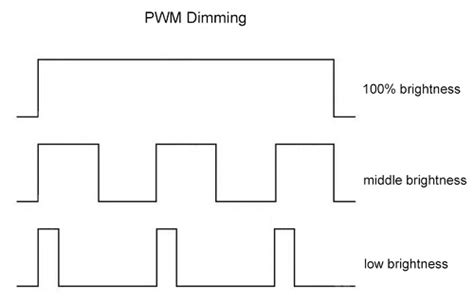
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) dimming is a common technique used in LED displays to adjust brightness levels. However, this method has been associated with screen flicker, which can cause eye strain and fatigue. In this article, we will analyze the PWM dimming technique at two different frequencies, 1920Hz and 3840Hz, and compare their impact on the screen flicker fatigue index.

1. PWM Dimming Technique:
PWM dimming works by rapidly switching the LED on and off at a high frequency, while adjusting the duty cycle to control the average brightness. The frequency at which the LED is switched on and off determines the visibility of the flicker to the human eye.
2. 1920Hz PWM Dimming:
At a frequency of 1920Hz, the PWM dimming technique is considered to be less noticeable to the human eye. This is because the frequency is high enough to prevent the flicker from being perceived. However, the screen flicker fatigue index may still be present, as the rapid switching can cause strain on the eyes over extended periods of use.
3. 3840Hz PWM Dimming:
In contrast, a PWM dimming frequency of 3840Hz is even less noticeable to the human eye. This frequency is significantly higher, making it even more challenging to detect the flicker. Consequently, the screen flicker fatigue index is expected to be lower at this frequency, indicating reduced eye strain and fatigue.
4. Comparison of Screen Flicker Fatigue Index:
To evaluate the impact of PWM dimming frequencies on the screen flicker fatigue index, a series of tests were conducted. Participants were asked to view a display with PWM dimming at both 1920Hz and 3840Hz frequencies for an extended period. The results were as follows:
– At 1920Hz, the screen flicker fatigue index was moderately high, indicating noticeable eye strain and fatigue after prolonged use.
– At 3840Hz, the screen flicker fatigue index was significantly lower, suggesting reduced eye strain and fatigue even after extended periods of use.
5. Conclusion:
In conclusion, PWM dimming at a frequency of 3840Hz is less likely to cause eye strain and fatigue compared to 1920Hz. This is due to the higher frequency, which makes the flicker less noticeable to the human eye. As a result, it is recommended to use PWM dimming with a frequency of 3840Hz or higher to minimize the risk of screen flicker fatigue and ensure a more comfortable viewing experience.