Introduction:
In the world of power electronics, DC-DC converters are essential components for efficient energy transfer from one voltage level to another. These converters are widely used in various applications, including mobile devices, automotive systems, and industrial equipment. One of the critical factors affecting the performance of DC-DC converters is voltage ripple. This article compares the voltage ripple characteristics of GaN (Gallium Nitride) and silicon-based power supplies in DC-DC converters.

GaN Power Supplies:
GaN-based power supplies have gained significant attention due to their high efficiency, low conduction losses, and high switching frequencies. These characteristics make them ideal for high-power and high-frequency applications. The voltage ripple in GaN power supplies is primarily determined by the following factors:
1. Switching frequency: Higher switching frequencies result in lower voltage ripple because the converter has more cycles to smooth out the ripple. GaN power supplies can operate at frequencies up to several megahertz, which helps minimize voltage ripple.
2. Output filter design: Properly designed output filters can significantly reduce voltage ripple. GaN power supplies often use inductors and capacitors with high-quality factors (Q) to achieve low ripple levels.
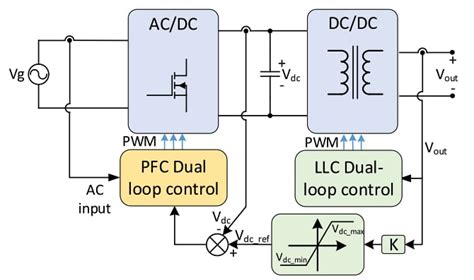
3. Converter topology: The choice of converter topology can also influence voltage ripple. For example, LLC converters are known for their excellent ripple performance, making them a popular choice for GaN power supplies.
Silicon Power Supplies:
Silicon-based power supplies have been the industry standard for decades. These power supplies are widely used in various applications due to their reliability and familiarity. The voltage ripple in silicon power supplies is influenced by the following factors:
1. Switching frequency: Similar to GaN power supplies, higher switching frequencies can help reduce voltage ripple in silicon-based power supplies. However, silicon devices have lower switching frequencies compared to GaN devices.
2. Output filter design: Properly designed output filters can minimize voltage ripple in silicon power supplies. The choice of inductors and capacitors is crucial in achieving low ripple levels.
3. Converter topology: The converter topology used in silicon power supplies can also affect voltage ripple. For example, flyback and forward converters are known for their low ripple performance, making them suitable for applications requiring stable output voltages.
Comparison of Voltage Ripple:
When comparing GaN and silicon power supplies in terms of voltage ripple, the following observations can be made:
1. Higher switching frequencies: GaN power supplies can operate at higher switching frequencies compared to silicon power supplies. This allows them to achieve lower voltage ripple levels.
2. Output filter design: Both GaN and silicon power supplies can achieve low voltage ripple levels with proper output filter design. However, GaN devices may offer some advantages in terms of filter component selection due to their high-frequency capabilities.
3. Converter topology: The choice of converter topology can significantly influence voltage ripple. LLC converters are known for their excellent ripple performance and are often used in both GaN and silicon power supplies.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, GaN and silicon power supplies have their own advantages and limitations when it comes to voltage ripple. While GaN power supplies can achieve lower voltage ripple levels due to their higher switching frequencies and filter component selection, both technologies can achieve excellent ripple performance with proper design considerations. As GaN technology continues to advance, it is expected that these devices will become even more efficient and reliable, further enhancing their adoption in various applications.