In the ever-evolving world of technology, the demand for energy-efficient and sustainable devices has never been higher. Wearables, in particular, have gained immense popularity due to their convenience and practicality. However, one of the biggest challenges faced by these devices is the need for a reliable power source. Enter the triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG), a revolutionary technology that could pave the way for self-powered wearables. This article delves into the latest breakthroughs in the field of triboelectric nanogenerators and their potential to revolutionize the wearables industry.
Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) are devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy through the triboelectric effect. This effect occurs when two materials are rubbed together, causing an accumulation of charge on their surfaces. By strategically designing the materials and structures of TENGs, scientists have been able to harness this effect to generate electricity.

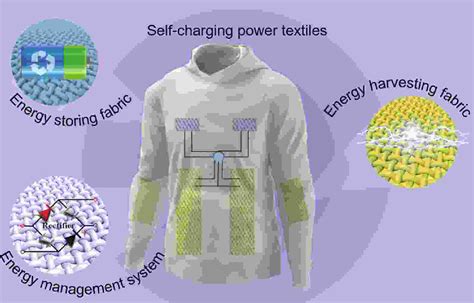
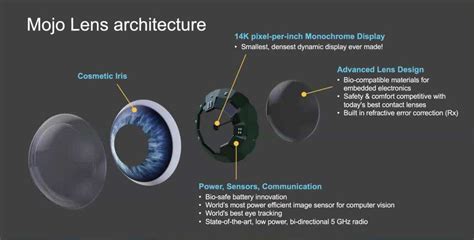
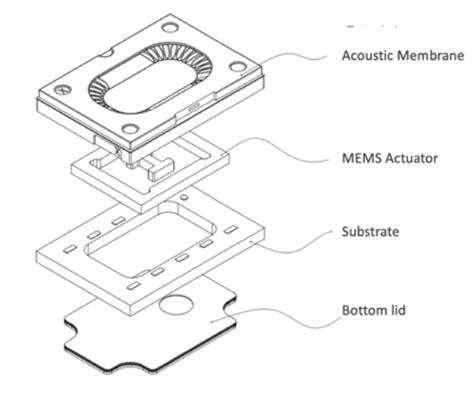
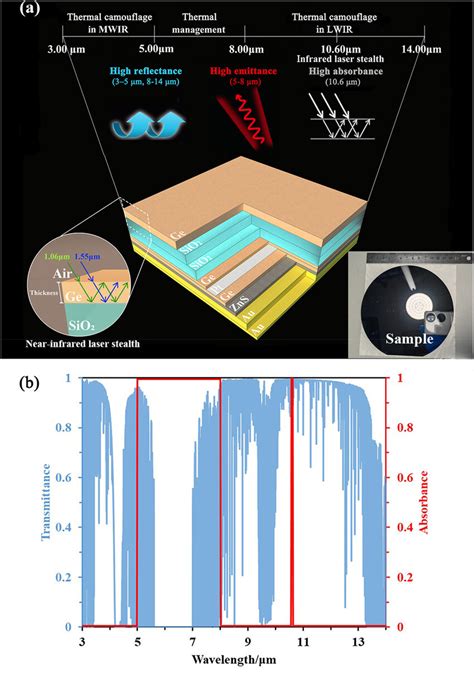
One of the most significant breakthroughs in the field of TENGs is the development of flexible and wearable devices. These devices can be seamlessly integrated into clothing or accessories, allowing for continuous energy generation without the need for external power sources. This has opened up a world of possibilities for self-powered wearables, such as smart fabrics, fitness trackers, and even smart clothing.
Another breakthrough in TENG technology is the enhancement of its energy conversion efficiency. Initially, TENGs had low conversion efficiencies, making them less practical for real-world applications. However, recent advancements have led to significant improvements in efficiency, making them a more viable option for powering wearables.
One of the key factors contributing to the improved efficiency of TENGs is the use of novel materials. For instance, researchers have discovered that certain polymers, when combined with metals or other conductive materials, can enhance the triboelectric effect and increase the energy output of TENGs. This has allowed for the development of more efficient and powerful TENGs, capable of powering a wide range of wearables.
Moreover, the integration of TENGs with other energy-harvesting technologies, such as solar cells and piezoelectric generators, has further expanded the potential of self-powered wearables. By combining the strengths of different energy-harvesting methods, these devices can achieve higher energy conversion rates and provide a more reliable power source.
Despite these advancements, there are still challenges to be addressed in the field of TENGs. One of the main concerns is the durability of the devices. Wearables are subjected to constant wear and tear, and TENGs must be able to withstand these conditions without losing their functionality. Researchers are actively working on developing more robust materials and structures to ensure the longevity of self-powered wearables.
Another challenge is the energy storage aspect. While TENGs can generate electricity, they often require energy storage devices, such as batteries, to store the generated energy for later use. Developing efficient and lightweight energy storage solutions is crucial for the widespread adoption of self-powered wearables.
In conclusion, the triboelectric nanogenerator has emerged as a groundbreaking technology with the potential to revolutionize the wearables industry. With ongoing advancements in material science, energy conversion efficiency, and durability, self-powered wearables are poised to become a reality. As these devices continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly transform the way we interact with technology, making it more energy-efficient, sustainable, and convenient than ever before.