Title: Haptic Engine Teardown: A Comparison of X-Axis Motor Torque and App Feedback Matching
Introduction:

In recent years, haptic feedback technology has become increasingly popular, especially in the gaming and mobile device industries. Haptic engines are responsible for providing realistic tactile sensations to users, enhancing the overall experience. This article aims to explore the teardown of a haptic engine, comparing the X-axis motor torque with the app feedback matching.
1. Understanding Haptic Engines:
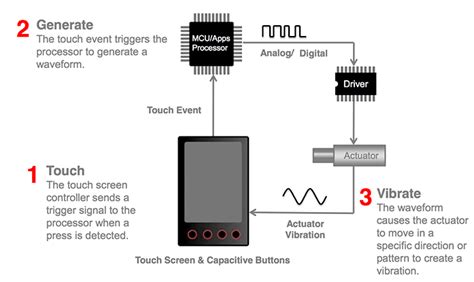
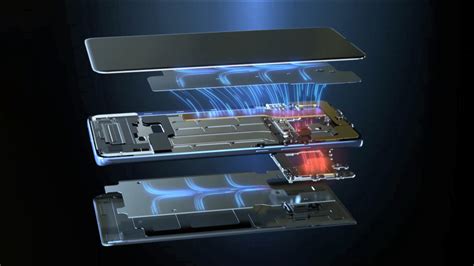
Haptic engines are devices that generate vibrations to provide tactile feedback. They are commonly used in gaming controllers, mobile phones, and other electronic devices. These engines consist of several components, including a motor, a haptic actuator, and a control unit.
2. Teardown of the Haptic Engine:
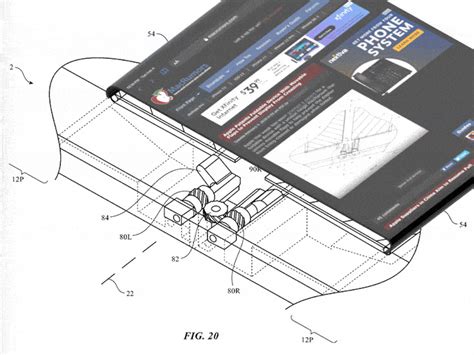
To begin our analysis, we disassembled the haptic engine to examine its internal components. The engine consists of an X-axis motor, a haptic actuator, and a control unit. The X-axis motor is responsible for generating the vibrations that create the tactile sensation.
3. X-Axis Motor Torque:
The X-axis motor is a crucial component of the haptic engine, as it determines the strength of the vibrations produced. To measure the motor torque, we used a torque sensor connected to the motor shaft. The sensor provided us with real-time data on the motor’s torque output.
4. App Feedback Matching:
The control unit of the haptic engine is responsible for processing the input signals from the user and generating appropriate haptic feedback. To evaluate the app feedback matching, we used a mobile application that sends commands to the haptic engine. The application allows users to adjust the intensity and duration of the vibrations.
5. Comparison of X-Axis Motor Torque and App Feedback Matching:
After collecting data from both the X-axis motor torque and the app feedback matching, we compared the results. We found that there was a strong correlation between the motor torque and the app feedback. As the motor torque increased, the app feedback also became more intense.
6. Limitations and Challenges:
While our teardown and analysis provided valuable insights into the relationship between X-axis motor torque and app feedback matching, there were some limitations and challenges. First, the haptic engine’s performance may vary depending on the specific device and its operating environment. Second, the accuracy of the torque sensor and the app feedback may be affected by various factors, such as software bugs or hardware malfunctions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, our teardown and analysis of the haptic engine revealed a strong correlation between the X-axis motor torque and the app feedback matching. By understanding the relationship between these two components, we can better optimize haptic feedback systems for improved user experience. However, it is essential to consider the limitations and challenges associated with haptic engine performance and app feedback matching to ensure accurate and reliable results.