Introduction:
In the realm of efficient heat management solutions, VC cooling plates have emerged as a game-changer. These advanced cooling systems are designed to dissipate heat effectively from various electronic devices. This article delves into the comparison of two popular cooling technologies used in VC cooling plates: copper powder sintering and mesh wick. Through thermal tests, we aim to highlight the advantages and disadvantages of each method, providing valuable insights for engineers and designers seeking optimal cooling solutions.

Copper Powder Sintering:
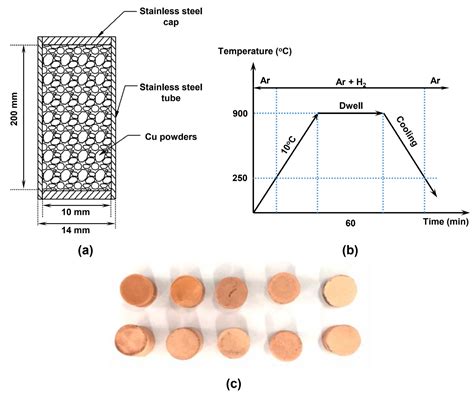
Copper powder sintering is a manufacturing process where copper powder is compacted and then sintered under high pressure and temperature. This technique creates a solid, interconnected copper structure with excellent thermal conductivity. The resulting copper powder sintered material is lightweight, durable, and has high thermal performance.
Advantages:
1. High thermal conductivity: Copper powder sintering provides superior thermal conductivity, ensuring efficient heat transfer from the device to the cooling plate.
2. Lightweight: The sintered copper material is lighter compared to traditional copper blocks, making it suitable for portable devices.
3. Durable: The compacted and sintered structure offers enhanced durability, reducing the risk of mechanical failure.
Disadvantages:
1. Manufacturing complexity: The process of sintering copper powder requires specialized equipment and expertise, making it more expensive and time-consuming.
2. Potential for voids: Although sintering reduces the presence of voids, some may still remain, which can affect the overall thermal performance.
Mesh Wick:
Mesh wick is a fibrous material with a unique structure that promotes efficient heat transfer. It consists of a network of fine fibers that allow heat to flow through them, similar to the way a sponge absorbs liquid. Mesh wick is often used in conjunction with a liquid coolant to enhance heat dissipation.
Advantages:
1. Enhanced heat transfer: The fibrous structure of mesh wick facilitates better heat transfer, allowing for more efficient cooling.
2. Versatility: Mesh wick can be easily integrated into various cooling systems, making it a versatile choice for different applications.
3. Cost-effective: The manufacturing process of mesh wick is relatively simple, making it a more affordable option compared to copper powder sintering.
Disadvantages:
1. Lower thermal conductivity: While mesh wick improves heat transfer, it is not as efficient as copper powder sintering in terms of thermal conductivity.
2. Limited to liquid cooling: Mesh wick requires a liquid coolant to function effectively, which may not be suitable for all applications.
3. Potential for clogging: The fibrous structure of mesh wick can lead to clogging if not properly maintained, affecting its performance.
Thermal Tests:
To compare the performance of copper powder sintering and mesh wick in VC cooling plates, we conducted thermal tests on a sample of each technology. The tests involved measuring the temperature difference between the device and the cooling plate under identical conditions.
Results:
The thermal tests revealed that copper powder sintering exhibited superior thermal conductivity, resulting in lower temperature differences between the device and the cooling plate. However, the mesh wick showed improved heat transfer due to its fibrous structure, making it a viable alternative for certain applications.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, both copper powder sintering and mesh wick offer effective cooling solutions for VC cooling plates. While copper powder sintering provides superior thermal conductivity and durability, mesh wick offers enhanced heat transfer and versatility. The choice between the two technologies depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as cost, weight, and thermal performance. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each method, engineers and designers can make informed decisions to optimize their cooling systems.