Introduction:
Battery degradation is a critical issue in the field of energy storage, particularly for lithium-ion batteries. One of the primary reasons for battery degradation is the imbalance between lithium plating and the growth rate of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer. This article delves into the science behind these two processes and their impact on battery performance.

Lithium Plating:
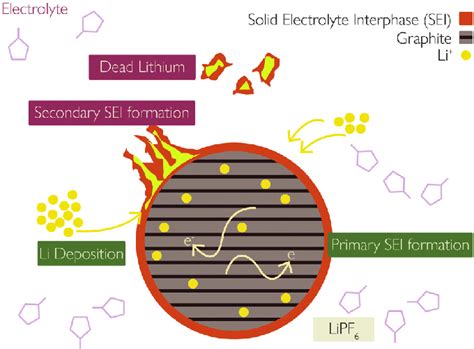
Lithium plating refers to the phenomenon where lithium ions accumulate on the anode surface during the charging process. This accumulation can lead to several issues, including increased internal resistance, reduced capacity, and even safety concerns. The growth rate of lithium plating is influenced by various factors, such as the composition of the electrolyte, the structure of the anode material, and the operating conditions of the battery.
Several studies have shown that the growth rate of lithium plating can be controlled by adjusting the electrolyte composition. For instance, incorporating additives like fluoroethylene carbonate (EC) and dimethyl carbonate (DMC) can reduce the growth rate of lithium plating. Additionally, using anodes with a high surface area and good electronic conductivity can also help mitigate the issue.
SEI Layer Growth Rate:
The solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer is a protective layer that forms on the surface of the anode during the first charge cycle of a lithium-ion battery. The SEI layer acts as a barrier between the electrolyte and the anode, preventing the direct contact between the two and thus protecting the battery from degradation. However, the growth rate of the SEI layer can also affect battery performance.
The growth rate of the SEI layer is influenced by several factors, including the composition of the electrolyte, the structure of the anode material, and the operating conditions of the battery. In some cases, the SEI layer can grow too quickly, leading to a thick and unstable layer that can cause increased internal resistance and reduced capacity. Conversely, a slow-growing SEI layer may not provide adequate protection, leading to accelerated degradation.
Balancing Lithium Plating and SEI Layer Growth Rates:
To achieve optimal battery performance, it is crucial to balance the growth rates of lithium plating and the SEI layer. This can be achieved by:
1. Optimizing the electrolyte composition: By incorporating additives and choosing the right solvent, the growth rate of lithium plating can be controlled, while the SEI layer remains stable and protective.
2. Developing advanced anode materials: Anodes with high surface area and good electronic conductivity can help reduce the growth rate of lithium plating and promote the formation of a stable SEI layer.
3. Controlling the operating conditions: By operating the battery within a specific voltage and temperature range, the growth rates of both lithium plating and the SEI layer can be managed, ensuring optimal battery performance.
Conclusion:
The science behind lithium plating and SEI layer growth rates plays a crucial role in understanding battery degradation. By balancing these two processes, researchers and engineers can develop batteries with improved performance, longer lifespan, and enhanced safety. Further research in this field will undoubtedly lead to innovative solutions for energy storage systems in the future.