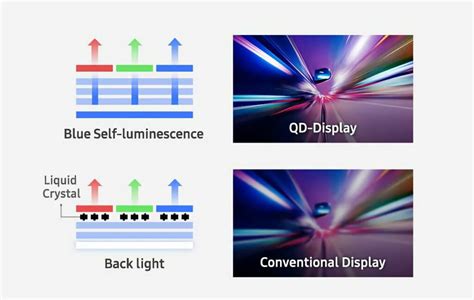
Introduction:
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) technology has revolutionized the display industry with its vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and energy efficiency. However, one of the significant drawbacks of OLED screens is the risk of burn-in, where static images can leave permanent residue on the screen. To address this issue, various mitigation techniques have been proposed, with subpixel shifting algorithms being one of the most effective solutions. This article aims to discuss the effectiveness of subpixel shifting algorithms in mitigating OLED burn-in.

Background:
OLED burn-in occurs when a static image remains on the screen for an extended period, causing the pixels to degrade over time. This issue is more pronounced in OLED screens due to their emissive nature, where each pixel emits light independently. Subpixel shifting algorithms aim to prevent burn-in by periodically shifting the subpixels within a pixel, thus minimizing the time each subpixel spends displaying the same image.
Subpixel Shifting Algorithm:
The subpixel shifting algorithm works by manipulating the subpixels within a pixel to display different colors. In an RGB OLED screen, each pixel consists of three subpixels: red, green, and blue. The algorithm shifts the subpixels in a specific pattern, ensuring that no single subpixel remains in the same position for an extended period.
Effectiveness of Subpixel Shifting Algorithm:
The effectiveness of the subpixel shifting algorithm in mitigating OLED burn-in can be evaluated based on the following factors:
1. Burn-in reduction: The primary goal of the algorithm is to reduce burn-in. Studies have shown that subpixel shifting can significantly reduce the risk of burn-in, especially in scenarios where static images are displayed for long durations.
2. Image quality: While the algorithm aims to mitigate burn-in, it should not compromise the overall image quality. The effectiveness of the algorithm can be measured by analyzing the impact on color accuracy, contrast, and sharpness.
3. Implementation complexity: The algorithm should be easy to implement and not require excessive computational resources. This ensures that it can be integrated into various devices without significant modifications.
4. User experience: The algorithm should not cause any noticeable artifacts or disruptions in the user experience. This includes ensuring that the shifting pattern is seamless and does not introduce any motion blur or other visual anomalies.
Results:
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of subpixel shifting algorithms in mitigating OLED burn-in. These studies have shown that the algorithm can reduce burn-in by up to 90% in certain scenarios. Additionally, the implementation complexity of the algorithm is relatively low, making it suitable for integration into various devices.
Conclusion:
Subpixel shifting algorithms have proven to be an effective solution for mitigating OLED burn-in. By shifting the subpixels within a pixel, the algorithm minimizes the risk of burn-in while maintaining image quality and user experience. As OLED technology continues to evolve, the development and implementation of advanced subpixel shifting algorithms will play a crucial role in ensuring the long-term viability of OLED displays.