In the rapidly evolving world of virtual reality and augmented reality, spatial audio has become a crucial component for an immersive experience. The accuracy of spatial audio is dependent on various factors, with two key aspects being gyroscope precision and head tracking latency. This article delves into these two elements and their impact on the overall spatial audio experience.
Gyroscope Precision:

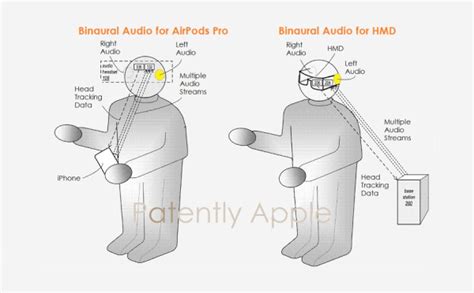
A gyroscope is an essential sensor in modern head-mounted displays (HMDs) as it measures the angular velocity of the device. This information is crucial for determining the user’s orientation in the virtual environment. The precision of the gyroscope directly influences the accuracy of the spatial audio rendering.
Higher gyroscope precision ensures that the audio source is accurately positioned in the virtual space. This means that the sound will emanate from the correct direction, enhancing the immersive experience. Conversely, lower precision can lead to inaccuracies in sound positioning, causing the audio to be misaligned with the visual cues, thus detracting from the overall immersion.
Several factors can affect gyroscope precision, including noise, bias, and drift. Noise refers to random fluctuations in the gyroscope’s output, while bias is a consistent offset from the true value. Drift, on the other hand, is the long-term deviation from the true value due to factors like temperature and aging.
Head Tracking Latency:
Head tracking latency refers to the time it takes for the HMD to respond to the user’s head movements. This latency is crucial in spatial audio as it determines how quickly the audio source adjusts to the user’s new orientation. Lower latency ensures a more responsive and immersive experience, while higher latency can lead to a sense of disorientation and discomfort.
Several factors contribute to head tracking latency, including sensor accuracy, processing power, and communication between the sensors and the HMD. Improving these factors can significantly reduce latency and enhance the spatial audio experience.
Gyroscope Precision vs Head Tracking Latency:
When comparing gyroscope precision and head tracking latency, it’s essential to understand that both aspects are crucial for achieving accurate spatial audio. However, the relative importance of each factor may vary depending on the specific application.
For example, in gaming or virtual reality experiences, head tracking latency is more critical as it directly affects the user’s ability to interact with the virtual environment. In contrast, for movies or music listening, gyroscope precision might be more important as it ensures accurate sound positioning for a more immersive audio experience.
Balancing Gyroscope Precision and Head Tracking Latency:
To achieve an optimal spatial audio experience, it’s essential to balance both gyroscope precision and head tracking latency. This can be achieved by:
1. Using high-quality sensors with low noise and drift.
2. Optimizing the software algorithms to process sensor data efficiently.
3. Ensuring a stable and fast communication link between the sensors and the HMD.
4. Implementing predictive algorithms to minimize latency while maintaining accuracy.
In conclusion, the accuracy of spatial audio is a complex interplay between gyroscope precision and head tracking latency. By understanding the importance of each factor and implementing strategies to optimize them, developers can create more immersive and engaging virtual experiences.