Introduction:
In the world of mini PCs, where compactness and efficiency are paramount, the choice of RAM can significantly impact performance. One of the most common dilemmas faced by users is whether to opt for a single-channel or dual-channel RAM configuration. This article delves into the performance loss associated with the single-channel RAM trap in mini PCs and compares it with the benefits of dual-channel configurations.

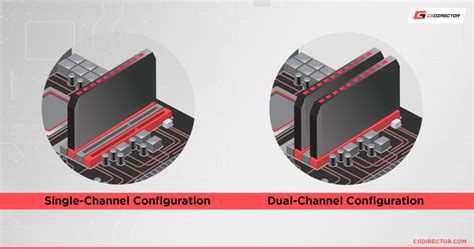
Single-Channel RAM: The Basics
Single-channel RAM refers to a configuration where the RAM operates on a single channel, leading to a potential bottleneck in data transfer between the RAM and the CPU. This setup is commonly found in mini PCs due to their limited physical space and power constraints.
Performance Loss in Single-Channel RAM
The primary drawback of single-channel RAM in mini PCs is the performance loss it incurs. When compared to dual-channel RAM, single-channel configurations struggle to keep up with the CPU’s processing demands. This results in slower data transfer rates, reduced multitasking capabilities, and overall suboptimal performance.
1. Slower Data Transfer Rates
Single-channel RAM operates on a single data path, which means that the CPU has to wait longer for data to be transferred between the RAM and itself. This delay can lead to slower application load times, increased latency, and reduced responsiveness in resource-intensive tasks.
2. Reduced Multitasking Capabilities
Single-channel RAM is ill-suited for multitasking scenarios. When running multiple applications simultaneously, the CPU has to constantly switch between tasks, leading to a higher likelihood of bottlenecks. This can cause applications to freeze or slow down, affecting the overall user experience.
3. Suboptimal Performance in Resource-Intensive Tasks
Resource-intensive tasks, such as video editing, gaming, and 3D rendering, require a significant amount of data to be processed in real-time. Single-channel RAM struggles to keep up with these demands, resulting in slower performance and subpar user experience.
Dual-Channel RAM: The Alternative
Dual-channel RAM, on the other hand, provides a more efficient data transfer path between the RAM and the CPU. By utilizing two separate channels, dual-channel RAM can significantly improve performance, especially in multitasking and resource-intensive scenarios.
Benefits of Dual-Channel RAM
1. Faster Data Transfer Rates
Dual-channel RAM operates on two separate data paths, allowing for faster data transfer rates between the RAM and the CPU. This results in reduced latency, improved application load times, and a smoother overall user experience.
2. Enhanced Multitasking Capabilities
With dual-channel RAM, the CPU can access data from both channels simultaneously, leading to better multitasking capabilities. This means that applications can run more efficiently, and the likelihood of bottlenecks is significantly reduced.
3. Improved Performance in Resource-Intensive Tasks
Resource-intensive tasks benefit greatly from dual-channel RAM. The increased data transfer rates allow the CPU to process more data in real-time, resulting in faster performance and a more enjoyable user experience.
Conclusion:
In the mini PC world, the choice between single-channel and dual-channel RAM can have a significant impact on performance. While single-channel RAM may be more compact and energy-efficient, it comes at the cost of performance loss. By opting for dual-channel RAM, users can enjoy faster data transfer rates, enhanced multitasking capabilities, and improved performance in resource-intensive tasks. Ultimately, the decision should be based on the specific needs and use cases of the mini PC user.