In the world of technology, the demand for refurbished gadgets has surged due to their affordability and environmental benefits. However, this growing market has also become a breeding ground for fraudulent activities, with one of the most common being battery cycle count tampering. This article delves into the intricacies of this issue and explores the methods used to detect such tampering.
What is Battery Cycle Count Tampering?

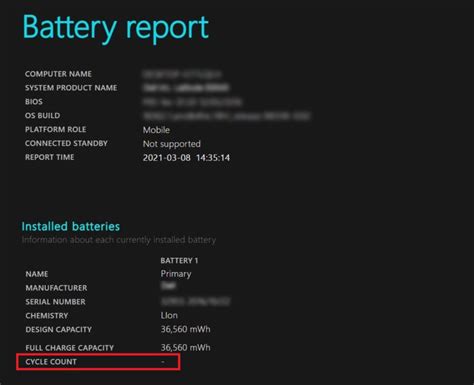
Battery cycle count tampering refers to the act of altering the number of charge-discharge cycles a battery has undergone, making it appear newer than it actually is. This practice is often employed by unscrupulous individuals or businesses to sell used devices at higher prices, misleading consumers into believing they are purchasing a product with a lower usage history.
Why is Battery Cycle Count Tampering a Concern?
Battery cycle count tampering poses several risks to consumers and the market as a whole:
1. Financial Loss: Consumers may end up paying more for a device that is older than advertised, leading to financial loss.
2. Safety Concerns: A battery with an inaccurate cycle count may have a shorter lifespan, posing safety risks due to potential overheating or failure.
3. Market Disruption: Unfair practices can disrupt the market, leading to a loss of trust in the refurbished tech industry.
Methods for Detecting Battery Cycle Count Tampering
To combat this issue, several methods have been developed to detect battery cycle count tampering:
1. Physical Inspection: A thorough physical examination of the device can sometimes reveal signs of tampering, such as scratches, glue residue, or unusual wear patterns on the battery.
2. Battery Testing: Advanced testing equipment can measure the battery’s capacity and discharge characteristics, providing an accurate cycle count. If the cycle count does not match the advertised usage, it may indicate tampering.
3. Software Analysis: Developers have created software tools that can analyze the device’s system logs and battery usage patterns to detect inconsistencies in the cycle count.
4. Blockchain Technology: By utilizing blockchain, manufacturers can create a secure, transparent, and immutable record of a battery’s cycle count, making it nearly impossible to tamper with.
5. Consumer Education: Educating consumers about the signs of battery cycle count tampering can empower them to make informed purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
Battery cycle count tampering is a significant concern in the refurbished tech market. By understanding the risks and implementing effective detection methods, we can ensure a fair and trustworthy marketplace for consumers and businesses alike. As technology continues to evolve, it is crucial to stay informed and vigilant to protect ourselves from fraudulent activities.