Introduction:
In the fast-paced world of data storage, two technologies have emerged as leaders in the mobile and consumer electronics markets: EMMC (Embedded MultiMediaCard) and UFS (Universal Flash Storage). Both technologies utilize NAND flash memory for data storage, but they differ in design, performance, and lifespan. This article aims to compare the lifespan NAND block management strategies employed by EMMC and UFS, highlighting their differences and implications for device manufacturers and consumers.

1. EMMC: A Brief Overview
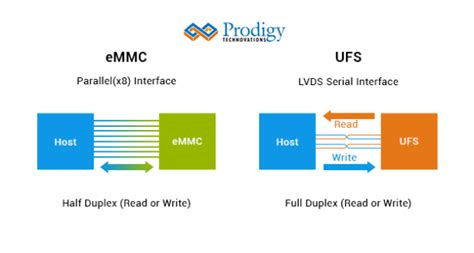
EMMC is a flash memory storage solution designed for mobile devices. It consists of a flash memory chip, a controller, and a connector. The controller is responsible for managing data transfer, error correction, and wear leveling, among other functions. EMMC has been widely used in smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices due to its compact size and low power consumption.
2. UFS: A Brief Overview
UFS, on the other hand, is a more advanced and powerful storage solution designed to meet the increasing demands of high-performance mobile devices. It offers faster data transfer rates, higher bandwidth, and more efficient power management compared to EMMC. UFS is becoming increasingly popular in flagship smartphones and other high-end devices.
3. Lifespan NAND Block Management Strategies
3.1 EMMC: Wear Leveling and Garbage Collection
EMMC devices use wear leveling to distribute write and erase cycles evenly across the NAND flash memory, ensuring that no single block wears out prematurely. This strategy extends the lifespan of the memory by preventing excessive writes to specific blocks.
Garbage collection is another critical aspect of EMMC’s lifespan management. It involves identifying and erasing unused data, freeing up blocks for future writes. This process helps to maintain the overall performance of the EMMC device over time.
3.2 UFS: Wear Leveling, Garbage Collection, and Intelligent Wear Management
UFS also employs wear leveling and garbage collection to manage the lifespan of its NAND flash memory. However, UFS introduces a more sophisticated approach called intelligent wear management.
Intelligent wear management is a combination of wear leveling and garbage collection strategies that adapt to the actual usage patterns of the device. This approach allows UFS to optimize the distribution of write and erase cycles, ensuring that the memory’s lifespan is maximized while maintaining high performance.
4. Comparison and Implications
4.1 Performance
UFS offers better performance compared to EMMC, with higher data transfer rates and bandwidth. This is due to its advanced architecture and the inclusion of features like multi-lane data transfer and command queuing.
4.2 Lifespan
Both EMMC and UFS have effective lifespan management strategies, but UFS is generally considered to have a longer lifespan due to its intelligent wear management and more efficient block management.
4.3 Cost and Market Adoption
EMMC is more cost-effective and has been widely adopted in the market, particularly for mid-range and budget devices. UFS, while offering superior performance and lifespan, is more expensive and is predominantly used in high-end devices.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, both EMMC and UFS are excellent storage solutions with their own strengths and weaknesses. EMMC is a cost-effective option for mid-range devices, while UFS offers superior performance and lifespan, making it ideal for high-end devices. As the mobile market continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how these technologies develop and what new advancements will be introduced in the future.