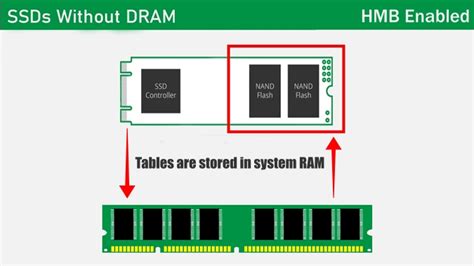
Title: SSD Cache Strategies: Addressing 4K Random Write Speed Drops in DRAM-less Drives
Introduction:

Solid State Drives (SSDs) have revolutionized the storage industry with their exceptional speed and reliability. However, as the demand for faster and more efficient SSDs continues to grow, manufacturers have been exploring new technologies and strategies to enhance performance. One significant challenge faced by the industry is the 4K random write speed drop in DRAM-less SSDs. This article delves into various SSD cache strategies that can help mitigate this issue.
1. SLC Cache:
Single-Level Cell (SLC) cache is a popular choice for DRAM-less SSDs. SLC cache stores frequently accessed data in a dedicated area of the SSD, allowing for faster read and write speeds. By employing SLC cache, SSDs can achieve higher 4K random write speeds and minimize the impact of the speed drop. However, SLC cache is more expensive and has limited capacity compared to other cache types.
2. TLC Cache:
Triple-Level Cell (TLC) cache is another option for DRAM-less SSDs. TLC cache offers a better cost-to-performance ratio than SLC cache, as it can store more data in the same physical space. However, it is slower and has a higher error rate compared to SLC cache. By using TLC cache, SSD manufacturers can achieve a balance between cost and performance while still addressing the 4K random write speed drop issue.
3. Pseudo-SLC Cache:
Pseudo-SLC cache is a caching technique that combines aspects of SLC and TLC caching. This method involves using SLC cache for the most frequently accessed data and TLC cache for less frequently accessed data. By doing so, SSDs can achieve higher 4K random write speeds while maintaining a lower cost compared to SLC cache alone. Pseudo-SLC cache is an effective strategy for DRAM-less SSDs, as it helps bridge the gap between performance and cost.
4. Wear Leveling and Garbage Collection:
Wear leveling and garbage collection are essential SSD management techniques that can also help mitigate the 4K random write speed drop issue. Wear leveling distributes write operations evenly across the SSD’s memory cells, extending the drive’s lifespan. Garbage collection removes unused data, freeing up space and improving performance. By optimizing these techniques, SSD manufacturers can enhance the overall performance of DRAM-less drives.
5. Advanced Flash Management:
Advanced flash management techniques, such as adaptive read and write algorithms, can also help address the 4K random write speed drop issue. These algorithms analyze the drive’s usage patterns and optimize the caching strategy accordingly. By dynamically adjusting the cache allocation based on the drive’s workload, manufacturers can achieve better performance and longevity.
Conclusion:
The 4K random write speed drop in DRAM-less SSDs is a significant challenge for the storage industry. However, by employing various SSD cache strategies, such as SLC cache, TLC cache, pseudo-SLC cache, wear leveling, garbage collection, and advanced flash management, manufacturers can address this issue effectively. These strategies help improve the overall performance and longevity of DRAM-less SSDs, ensuring that users can enjoy the benefits of faster and more efficient storage solutions.